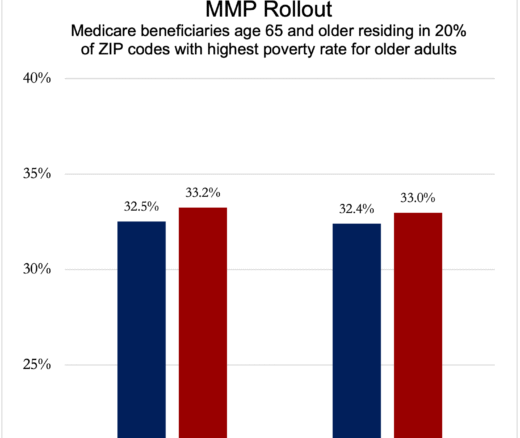
Integrated Care Plans Didn’t Boost Medicaid Enrollment for the Poorest Seniors
Chart of the Day: Medicare-Medicaid Plans—Created to Streamline Care for Dually Eligible Individuals—Failed to Increase Medicaid Participation in High-Poverty Communities
Blog Post
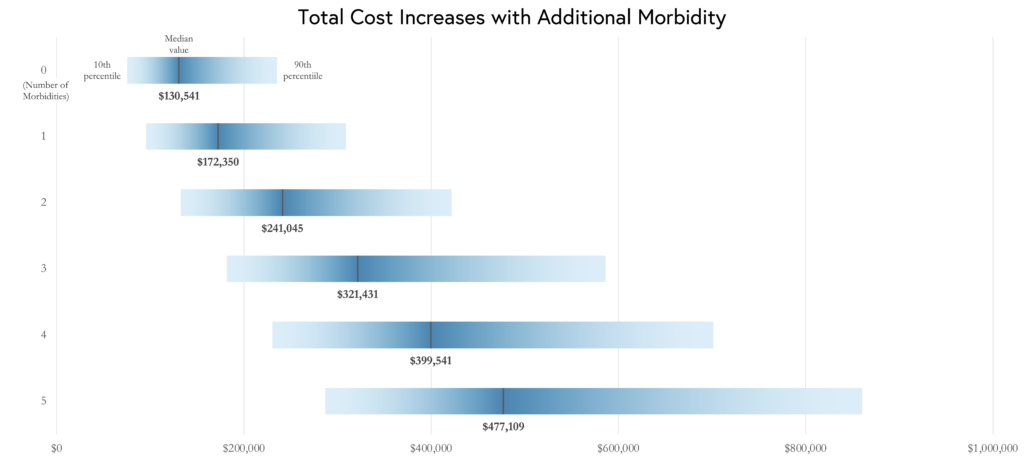
Each year, there are approximately 380,000 premature births, which carry high costs and substantial economic impact, especially for those born extremely preterm. A recent study using data from California hospitals quantified the financial consequences, citing a median cost of $269,974 per patient. Prior studies have examined the costs of prematurity, but few have addressed how the presence of specific complications influences cost.
In a new Journal of Pediatrics study, LDI Senior Fellow Scott Lorch and colleague Kuan-Chi Lai evaluate the costs of five of the most common complications associated with premature birth in a national sample derived from 30 children’s hospitals between 2009 and 2018.
The investigators found that birth costs were significantly higher in the presence of one complication and that costs increased as the number of complications increased. Additionally, they found that birth costs attributed to complications stemmed from both greater use of health care services and longer length of stay.
Ultimately, this study quantifies the cost of preterm birth. As costs increase with earlier births, innovative strategies that prevent preterm births are valuable and worth investigating.
The study, “Health Care Costs of Major Morbidities Associated with Prematurity in United States Children’s Hospitals,” was published on December 9, 2022 in The Journal of Pediatrics. Authors include Kuan-Chi Lai and Scott Lorch.


Chart of the Day: Medicare-Medicaid Plans—Created to Streamline Care for Dually Eligible Individuals—Failed to Increase Medicaid Participation in High-Poverty Communities
Research Brief: Shorter Stays in Skilled Nursing Facilities and Less Home Health Didn’t Lead to Worse Outcomes, Pointing to Opportunities for Traditional Medicare

How Threatened Reproductive Rights Pushed More Pennsylvanians Toward Sterilization

Abortion Restrictions Can Backfire, Pushing Families to End Pregnancies

They Reduce Coverage, Not Costs, History Shows. Smarter Incentives Would Encourage the Private Sector
Research Brief: Less Than 1% of Clinical Practices Provide 80% of Outpatient Services for Dually Eligible Individuals