
Impact: LDI Fellows Shaped Public Discussion and Public Policy in 2025
Highlighting 10 Ways LDI Fellows Put Their Research Into Action
Blog Post

On February 7, 2025, the Trump administration abruptly announced a cap on indirect rates for National Institutes of Health (NIH) awards, limiting them to 15%—a move currently on hold following a district court injunction temporarily blocking the policy. While NIH funding has long enjoyed bipartisan support, it is once again under threat. Today’s Chart of the Day places this controversy in a broader context by showing how NIH funding has already eroded over the past two decades.
In a recent JAMA Viewpoint, Penn LDI Senior Fellow Nadir Yehya notes that between 1998 and 2003, the NIH budget doubled in nominal terms—the actual dollar amounts spent or allocated each year, not adjusted for inflation. This period was marked by robust bipartisan investment in biomedical research. But that rapid growth proved short-lived. Since peaking in 2003, the NIH budget has stagnated or declined in real dollars, meaning figures adjusted for inflation using the Consumer Price Index (CPI), even as the U.S. population grew by nearly 50 million and research costs rose sharply.
By 2024, the NIH budget in real terms stood about 7.4% lower than its 2003 peak, underscoring a sustained failure to keep pace with inflation and the rising cost of scientific research. As policymakers weigh potential cuts, this inflation-adjusted trajectory is a critical data point for setting funding priorities that reflect the long-term needs of the biomedical research enterprise.
The study, “NIH Funding Has Stagnated Since 2003,” was published on April 16, 2025, in JAMA. Authors include Nadir Yehya.


Highlighting 10 Ways LDI Fellows Put Their Research Into Action

From AI-Powered Public Health Messaging to Stark Divides in Child Wellness and Medicaid Access, LDI Experts Highlight Urgent Problems and Compelling Solutions

An LDI Expert Offers Three Recommendations That Address Core Criticisms of the ACA’s Model

Administrative Hurdles, Not Just Income Rules, Shape Who Gets Food Assistance, LDI Fellows Show—Underscoring Policy’s Power to Affect Food Insecurity
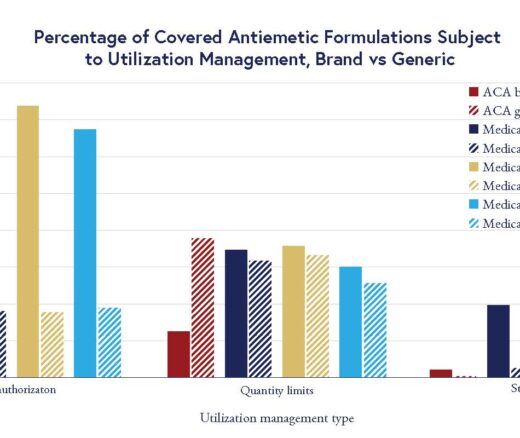
Chart of the Day: LDI Researchers Report Major Coverage Differences Across ACA and Medicaid Plans, Affecting Access to Drugs That Treat Chemo-Related Nausea

A Penn LDI Virtual Panel Looks Ahead at New Possibilities