Over 500 U.S. Hospitals Have Stopped Delivering Babies Since 2010
A Crisis in Maternal Care is Unfolding—and it’s Hitting Rural and Urban Communities Alike
Health Care Access & Coverage | Population Health
Blog Post
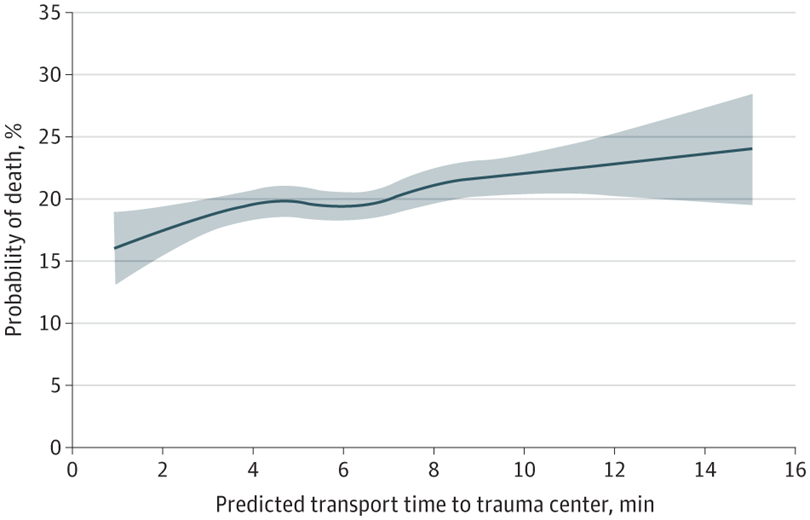
Firearm violence is a public health crisis that continues to worsen in the United States. This crisis has escalated significantly with the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic, further stressing our communities. Patients injured by firearms require rapid transport to trauma centers for life-saving procedures. For these critically injured patients, truly every minute counts. In a new JAMA Surgery study, LDI Senior Fellows Elinore Kaufman and Jeremy Cannon, along with their colleagues, found that longer predicted transport time to a trauma center is associated with higher rates of death.
If time is so important, what might local policymakers do to reduce the time to care? Philadelphia utilizes a practice known as “scoop and run.” In a previous study, Dr. Cannon found that if police officers were the first to arrive at a firearm injury scene, the most severe injuries were more likely to be alive on arrival to the hospital when transported by police. What this study points out is that time is a critical factor, and systems need to focus on reducing the time to care as much as possible to reduce deaths from gun violence in U.S. cities.
The study, “Association Between Geospatial Access to Care and Firearm Injury Mortality in Philadelphia,” was published on August 24, 2022, in JAMA Surgery. Authors include James P. Byrne, Elinore Kaufman, Dane Scantling, Vicky Tam, Niels Martin, Shariq Raza, Jeremy Cannon, C. William Schwab, Patrick M. Reilly, and Mark J. Seamon.


A Crisis in Maternal Care is Unfolding—and it’s Hitting Rural and Urban Communities Alike

Stable Payments Improved Margins But Not Liquidity, New LDI Analysis Finds

LDI Senior Fellow Cited for “Significant Contributions” in Research

Outdated Laws Target Black and Queer Lives in Over 30 States, Fueling a Deadly Disease

Selected for Current and Future Research in the Science of Amputee Care

Research Memo: Delivered to House Speaker Mike Johnson and Majority Leader John Thune